Hey all! It’s been a long time since I haven’t written a blog about Kubernetes. So I was wandering in r/devops in Reddit and saw a post where the digital ocean is hosting a Kubernetes challenge and guess what they’re giving away free credits of $120 to try it out free!!!
This blog is written in multiple sections from steps to apply to steps to deploy your app in Digital Ocean Kubernetes via CI/CD. Let’s get started!
Challenge Details
- Link of the challenge page Here
- Pick one challenge from the list mention in above link based on your knowledge.
- Create a GitHub or GitLab repo for your project
- Fill out the code challenge form to get DigitalOcean credits for your project
- Join the #kubernetes-challenge channel in the DigitalOcean Deploy Discord
- Complete your challenge
- Write about what you’ve built and share it on a blog or in your project README.
- Make a pull request against the Kubernetes Challenge Github Repo with information about your project
- Let them know you’ve completed your challenge by filling out this form
Now that we’ve applied let’s take a look at one of the challenges I chose :
Deploy a GitOps CI/CD implementation
GitOps is the (only) way automate deployment pipelines for Kubernetes environments in 2022, and ArgoCD is currently one of the leading player. Install it to create a CI/CD solution, using GH Actions for actual image building.
Cluster Creation
- Sign in to your DO console.
- Click on NEW button and create a Kubernetes cluster with default values.
- You can customize the location of cluster nearest to your location to avoid altency issues to API server.
- Once you submit, it’ll take around 10-15 min for the worker nodes and API server to become ready.
- Click on the Actions button and download the kubeconfig file.
- Once you download, install kubectl binary by following steps in the Getting started section of *overview *tab.
- Once, kubectl in installed in your local, you can save / move the config file downloaded to your
~/.kube/configlocation. - Now, you can connect to your API server, test it by running :
kubectl get node -o wide

Project setup
- Clone this repository using below command :
git clone https://github.com/tanmay-bhat/DigitalOcean-Kubernetes-Challenge-argoCD
-
This project contains below:
- go app
- Dockerfile
- github actions file ( CI)
- Kubernetes manifest files
Let’s Look mainly kustomize/base :
- Here, Deployment.yaml file contains the deployment resource YAML file.
containers:
- image: registry.digitalocean.com/tanmaybhat/saymyname
name: saymyname
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 8080
imagePullSecrets:
- name: tanmaybhat
-
Notice the image registry I’m using is the Digital Ocean registry itself and not the mostly used Docker Hub.
-
The ImagePullSecrets has a name: Tanmay Bhat. This is the Kubernetes secret which has the Digital Ocean registry credentials which we will use to pull the image.
-
Now let’s look at our Github actions config file :
name: Go
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
tags:
- 'v*.*.*'
jobs:
build:
name: Build
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Set up Go 1.x
uses: actions/setup-go@v2
with:
go-version: ^1.14
- name: Check out code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Extract Git Tag
run: echo "GIT_TAG=${GITHUB_REF/refs\/tags\//}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Login to Digitalocean
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: registry.digitalocean.com
username: ${{ secrets.DIGITAL_OCEAN_TOKEN }}
password: ${{ secrets.DIGITAL_OCEAN_TOKEN }}
- name: push image to digitalocean
run: |
docker build -t registry.digitalocean.com/tanmaybhat/saymyname:${{ env.GIT_TAG }} .
docker push registry.digitalocean.com/tanmaybhat/saymyname:${{ env.GIT_TAG }}
deploy:
name: Deploy
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: build
steps:
- name: Check out code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Extract Git Tag
run: echo "GIT_TAG=${GITHUB_REF/refs\/tags\//}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: update image tag in manifest
uses: imranismail/setup-kustomize@v1
- run: |
cd kustomize/base
kustomize edit set image registry.digitalocean.com/tanmaybhat/saymyname:${{ env.GIT_TAG }}
- name: Commit files
run: |
git config --local user.email "action@github.com"
git config --local user.name "GitHub Action"
git commit -am "update image tag to ${{ env.GIT_TAG }}"
- name: Push changes
uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
with:
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
I’m gonna explain the above section since the main goal of this article is to do CI/CD :
- The on section says trigger this piepline if the chnages has been pushed to **Main branch with a tag in format : vx.x.x ( i.e v1.0.0 etc)
- On each tag push, pipeline will run 2 jobs. Build and Deploy.
- In Build section, the follwing steps will run on ubuntu image.
- Check out code step uses pre-build action
actions/checkout@v2to clone current repository into the piepline container i.e ubuntu. - Extract Git Tag is used to get the latest tag pusued to main branch and store it in th environmental variable GIT_TAG.
- In Login to Digitalocean, since we need to push our build docker images to a private registry like Digital Ocean, I’m using docker login action to auttenticate to the DO registry.
- In push image to digitalocean, I’m buidling the docker image and tagging it to latest pushed tag version and pushing to my registry.
- Next comes, the Deploy section. here again I’m using ubuntu as base image and again getting the repository from main branch and extracting tag version from the repositiry.
- Once that is done, I’ll use a tool called Kustomize to update my manifest file’s docker image tag to the latest tag version.
- If you’re using helm charts only but not kustomize with Helm, you need to use Sed command and update the image tag in manifest file ( deployment.yaml).
- Later, I’m doing the commit of latest tag edit and pushing the changes back to my repo.
To sum up, what the exact pipeline does whenever a new tag is pushed to main branch :
- clone the repository, build the docker image, tag it and push it to registry.
- update the tag in manifest file and push it back to gthe repository.
You might have this question, Tanmay, this is just CI, where’s CD ? well, that’s the magic ArgoCD solves for us.
ArgoCD
- Setup ArgoCD by running the below commands :
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
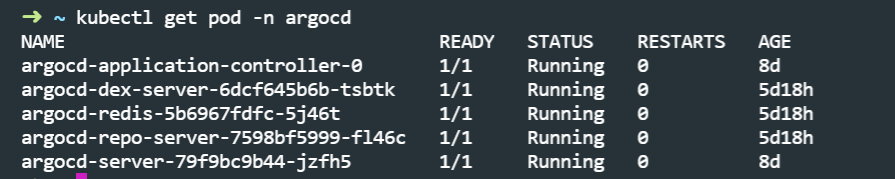
- Once done, you can verify its running status by running the command
- Next step is to retrieve the password of argocd. For that, run :
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
- By default argocd service type will be ClusterIP. That means you cant access argocd outside of your cluster. So, Let’s change that to LoadBalancer by running :
kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "LoadBalancer"}}'
- Now, wait for couple more minutes for LoadBalancer to start in Digital Ocean and get the endpoint of it by running :

- Open the external IP in your browser and voila, you should see argocd UI login page. Login with username: admin password got from step 3.
ArgoCD Configuration
- Once logged in to ArgoCD UI, click on new app and set the below values:
application name : demo-argocd
Project : default
Sync Policy : Automatic
Repository URL : <GITHUB REPO URL OF YOUR PROJECT>
Rivision : HEAD
Path : kustomize/base
Destination Cluster : https://kubernetes.default.svc
Namespace : default
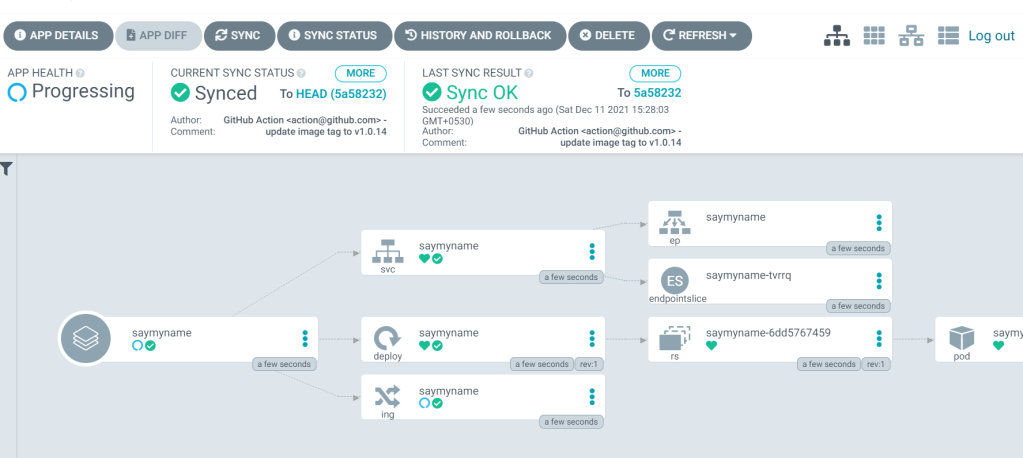
Click create and see your app glowing in your cluster.
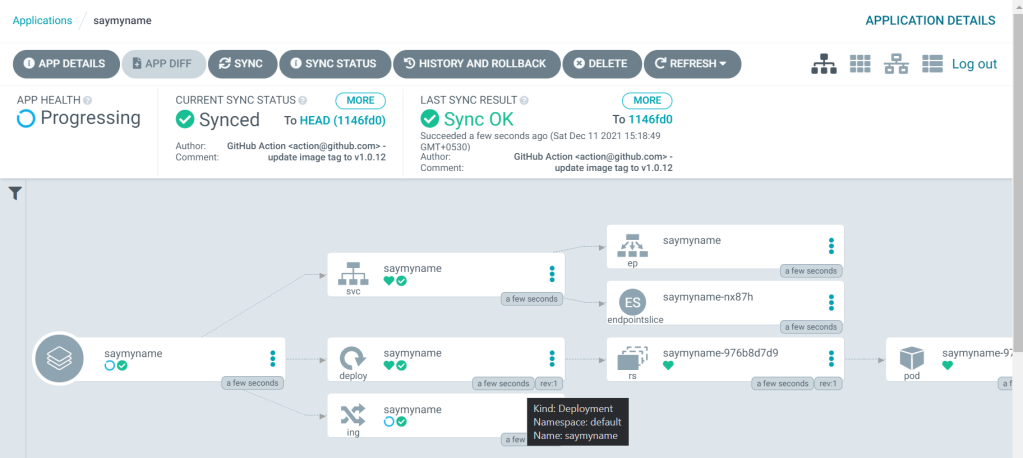
the ArgoCD magic here is that, it watches for any new changes to your repo every 3 minutes ( default ) and new changes will be auto-applied in your cluster.
See the comment that says: update the tag to v1.0.12 ? that was my last commit. If a new tag is committed, here’s how it’s gonna update and look
Conclusion
I found DOKS to be extreme easy to set up and straightforward. From click to integrate Registry to a Kubernetes cluster, easy cluster creation and scaling up.